图的遍历(graph traversal)
一、图的遍历
从图中某一顶点出发系统地访问图中所有顶点,使每个顶点恰好被访问一次,这种运算操作被称为图的遍历。为了避免重复访问顶点,需要记录已访问过的顶点。
图的遍历分为深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历
二、深度优先遍历(DFS)
从图中某结点出发,访问其相邻结点(按编号最小或最大),再访问该结点的相邻结点 ,直至访问完所有的结点。一条路走到头,回头再走没走过的路。可以看出DFS算法是一个递归的过程,其中需要借助一个栈完成操作。
基于邻接表的遍历的序列不唯一,基于邻接矩阵的遍历序列是唯一的。
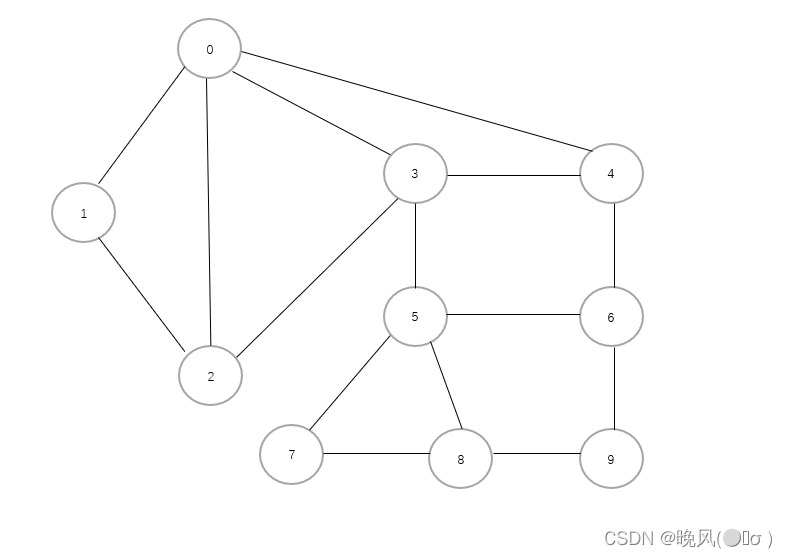
深度优先遍历(从大到小):0,4,6,9,8,7,5,3,2,1。
深度优先遍历(从小到大):0,1,2,3,4,6,5,7,8,9。
图的深度遍历-邻接表+递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 | /**************************************************************** * 代码作者: Alex Li * 创建时间: 2025-01-12 12:20:35 * 最后修改: 2025-01-12 12:30:27 * 文件描述: 图的深度遍历-邻接表+递归 ****************************************************************/ #include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; void DFS(vector<vector<int>>& adjList, int vertex, vector<bool>& visited) { // 将当前顶点标记为已访问 visited[vertex] = true; // 处理当前顶点 cout << vertex << " "; // 递归访问所有未访问的邻接顶点 for (int neighbor : adjList[vertex]) { if (!visited[neighbor]) { DFS(adjList, neighbor, visited); } } } int main() { // 创建一个有4个顶点和4条边的图的邻接表 vector<vector<int>> adjList(4); adjList[0].push_back(1); adjList[1].push_back(0); adjList[1].push_back(2); adjList[2].push_back(1); adjList[2].push_back(3); adjList[3].push_back(2); // 创建一个布尔向量来跟踪访问状态 vector<bool> visited(4, false); // 从顶点 0 开始执行深度优先搜索 DFS(adjList, 0, visited); return 0; } |
图的深度遍历-邻接表+栈
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 | /**************************************************************** * 代码作者: Alex Li * 创建时间: 2025-01-12 12:33:40 * 最后修改: 2025-01-12 12:43:19 * 文件描述: 图的深度搜索-邻接表+栈 ****************************************************************/ #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <stack> using namespace std; void DFS(vector<vector<int>>& adjList, int startVertex) { // 创建一个布尔向量,用于跟踪是否访问过顶点 vector<bool> visited(adjList.size(), false); // 使用显式栈保存顶点,用于模拟递归调用的行为 stack<int> s; // 将起始顶点入栈 s.push(startVertex); while (!s.empty()) { // 取出栈顶元素 int vertex = s.top(); s.pop(); // 如果顶点还未被访问,处理它并标记为已访问 if (!visited[vertex]) { cout << vertex << " "; // 处理当前顶点 visited[vertex] = true; } // 将所有未访问的邻接顶点入栈 for (int neighbor : adjList[vertex]) { if (!visited[neighbor]) { s.push(neighbor); } } } } int main() { // 创建一个有4个顶点和4条边的图的邻接表 vector<vector<int>> adjList(4); adjList[0].push_back(1); adjList[1].push_back(0); adjList[1].push_back(2); adjList[2].push_back(1); adjList[2].push_back(3); adjList[3].push_back(2); // 从顶点0开始执行深度优先搜索 DFS(adjList, 0); return 0; } |
递归和显式栈的比较
| 特点 | 递归实现 | 显式栈实现 |
|---|---|---|
| 代码简洁性 | 更简洁,逻辑直接 | 需要手动管理栈,代码稍显复杂 |
| 函数调用栈 | 利用函数调用栈 | 使用显式栈替代函数调用栈 |
| 栈溢出问题 | 如果递归深度过大,可能导致栈溢出 | 不依赖函数栈,避免溢出问题 |
| 适用场景 | 图较小,递归深度有限 | 图较大,递归深度可能超过限制 |
五、图的深度遍历-邻接矩阵+栈
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 | /**************************************************************** * 代码作者: Alex Li * 创建时间: 2025-01-12 12:48:24 * 最后修改: 2025-01-12 12:48:54 * 文件描述: 图的深度搜索 邻接矩阵+栈 ****************************************************************/ #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <stack> using namespace std; void DFS(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int startVertex) { int n = matrix.size(); // 顶点个数 vector<bool> visited(n, false); // 标记访问状态 stack<int> s; // 显式栈 // 将起始顶点压入栈 s.push(startVertex); while (!s.empty()) { // 获取栈顶元素 int vertex = s.top(); s.pop(); // 如果当前顶点未被访问,则处理它 if (!visited[vertex]) { cout << vertex << " "; // 处理当前顶点 visited[vertex] = true; // 标记为已访问 } // 遍历邻接矩阵中当前顶点的所有邻居 // 注意要从高到低遍历,保证栈的深度优先顺序 for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; --i) { if (matrix[vertex][i] == 1 && !visited[i]) { s.push(i); // 将未访问的邻居压入栈 } } } } int main() { // 定义一个4个顶点的图(邻接矩阵表示) vector<vector<int>> matrix = { {0, 1, 0, 0}, // 顶点 0 {1, 0, 1, 0}, // 顶点 1 {0, 1, 0, 1}, // 顶点 2 {0, 0, 1, 0} // 顶点 3 }; // 从顶点 0 开始深度优先遍历 cout << "DFS Traversal: "; DFS(matrix, 0); return 0; } |
三、广度优先遍历(BFS)
图的广度遍历-邻接表+队列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 | /**************************************************************** * 代码作者: Alex Li * 创建时间: 2025-01-12 13:04:08 * 最后修改: 2025-01-12 13:05:17 * 文件描述: 图的BFS,邻接表+队列 ****************************************************************/ #include <iostream> #include <queue> #include <vector> using namespace std; const int MAX_VERTICES = 1000; void BFS(vector<int>* adjList, int numVertices, int startVertex) { // 创建一个数组用于记录哪些顶点已经被访问 bool visited[MAX_VERTICES] = { false }; // 创建一个队列用于存储待处理的顶点 queue<int> q; // 将起始顶点标记为已访问并加入队列 visited[startVertex] = true; q.push(startVertex); // 开始处理队列中的顶点 while (!q.empty()) { // 从队列中取出下一个顶点 int vertex = q.front(); q.pop(); // 处理当前顶点 cout << vertex << " "; // 将当前顶点所有未访问的邻居加入队列 for (int i = 0; i < adjList[vertex].size(); ++i) { int neighbor = adjList[vertex][i]; if (!visited[neighbor]) { visited[neighbor] = true; // 标记邻居为已访问 q.push(neighbor); // 将邻居加入队列 } } } } int main() { // 创建一个有4个顶点和4条边的图的邻接表 int numVertices = 4; vector<int> adjList[MAX_VERTICES]; adjList[0].push_back(1); // 顶点0连接顶点1 adjList[1].push_back(0); // 顶点1连接顶点0 adjList[1].push_back(2); // 顶点1连接顶点2 adjList[2].push_back(1); // 顶点2连接顶点1 adjList[2].push_back(3); // 顶点2连接顶点3 adjList[3].push_back(2); // 顶点3连接顶点2 // 从顶点0开始执行广度优先搜索 BFS(adjList, numVertices, 0); return 0; } |
图的广度遍历-邻接矩阵+队列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 | /**************************************************************** * 代码作者: Alex Li * 创建时间: 2025-01-12 13:07:43 * 最后修改: 2025-01-12 13:07:47 * 文件描述: 图的广度优先搜索 邻接矩阵+队列 ****************************************************************/ #include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std; const int MAX_VERTICES = 1000; void BFS(int adjMatrix[][MAX_VERTICES], int numVertices, int startVertex) { // 创建一个数组用于记录哪些顶点已经被访问 bool visited[MAX_VERTICES] = { false }; // 创建一个队列用于存储待处理的顶点 queue<int> q; // 将起始顶点标记为已访问,并将其加入队列 visited[startVertex] = true; q.push(startVertex); // 开始处理队列中的顶点 while (!q.empty()) { // 从队列中取出下一个顶点 int vertex = q.front(); q.pop(); // 处理当前顶点 cout << vertex << " "; // 将当前顶点的所有未访问邻居加入队列 for (int i = 0; i < numVertices; ++i) { if (adjMatrix[vertex][i] == 1 && !visited[i]) { visited[i] = true; // 标记邻居为已访问 q.push(i); // 将邻居加入队列 } } } } int main() { // 创建一个有4个顶点和4条边的图的邻接矩阵 int numVertices = 4; int adjMatrix[MAX_VERTICES][MAX_VERTICES] = { { 0, 1, 0, 0 }, // 顶点 0 的邻接情况 { 1, 0, 1, 0 }, // 顶点 1 的邻接情况 { 0, 1, 0, 1 }, // 顶点 2 的邻接情况 { 0, 0, 1, 0 } // 顶点 3 的邻接情况 }; // 从顶点0开始执行广度优先搜索 BFS(adjMatrix, numVertices, 0); return 0; } |
